Debugging and Inspection
Installation
Add the browser extension for chrome extension or firefox extension
Open dev tools
After installing and loading your site in dev-mode, you either click the Data Client logo (default bottom-right of window) or the redux-devtool logo in the location bar.
Clicking that will open the inspector, which allows you to observe dispatched actions, their effect on the store's state as well as current store state.
The Data Client logo only appears in dev-mode. However, its location can be moved or completely disabled by setting the devButton DataProvider prop.
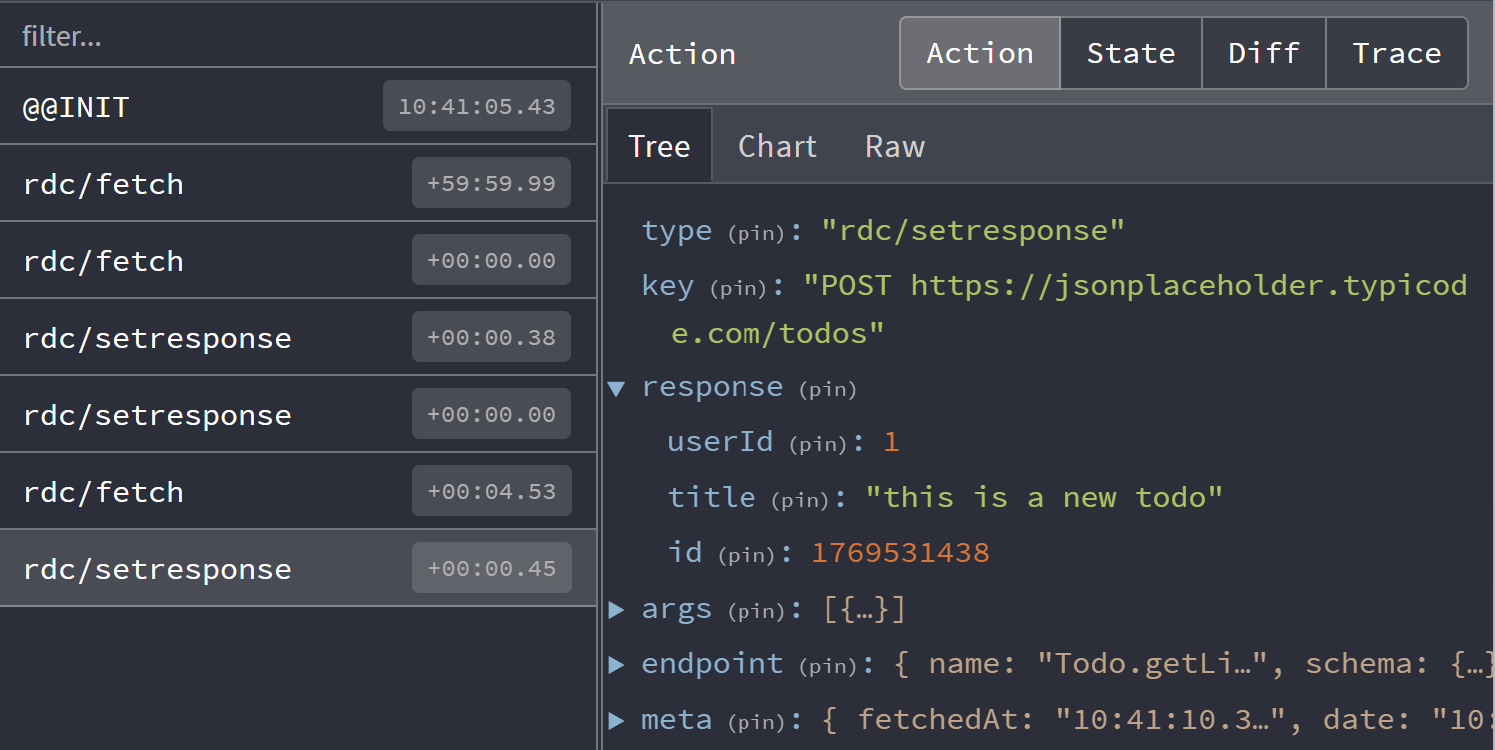
The Controller dispatches actions, making that page useful for understanding what actions you see. Here we observe common actions of fetch and setResponse.
By default the devtool integration will filter duplicate fetch actions. This can be changed with skipLogging option.
Control flow
Data Client uses the flux store pattern, making debugging straightforward as each change is traceable and descriptive.
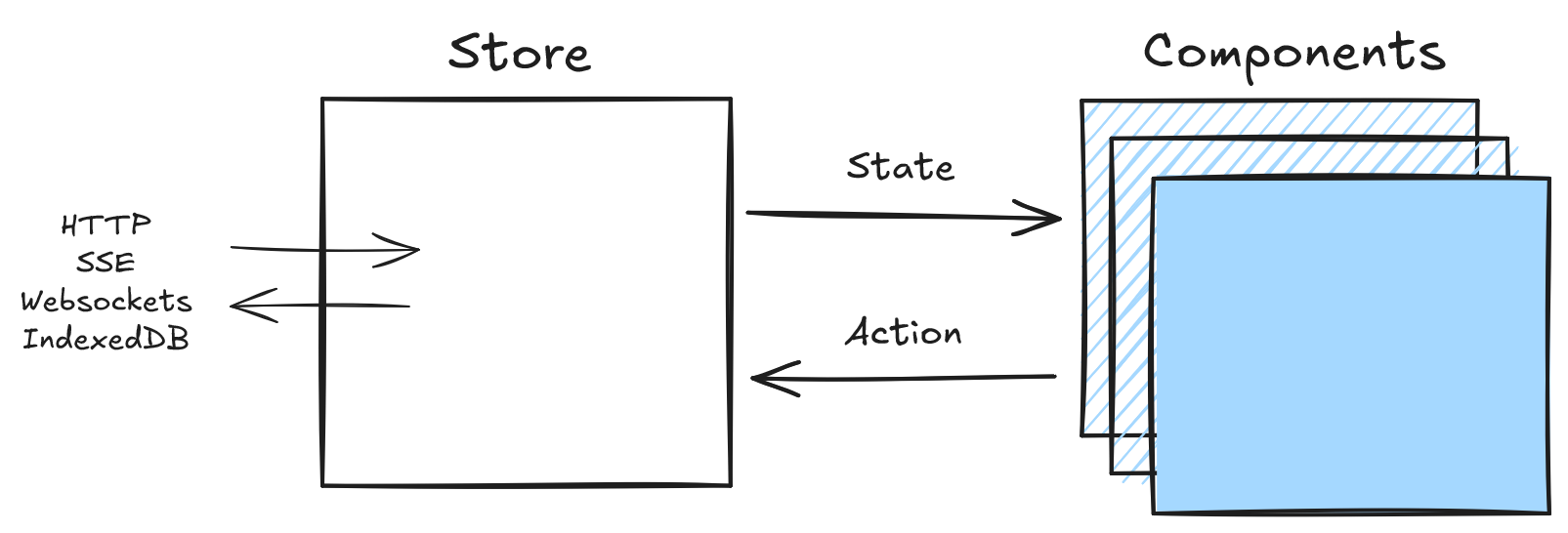
State Inspection
Whens schemas are used, responses are normalized into entities
and endpoints tables. This enables automatic performance advantages over simpler key-value fetch caches; especially
beneficial with dynamic (changing) data. This also eliminates data-inconsistency bugs.
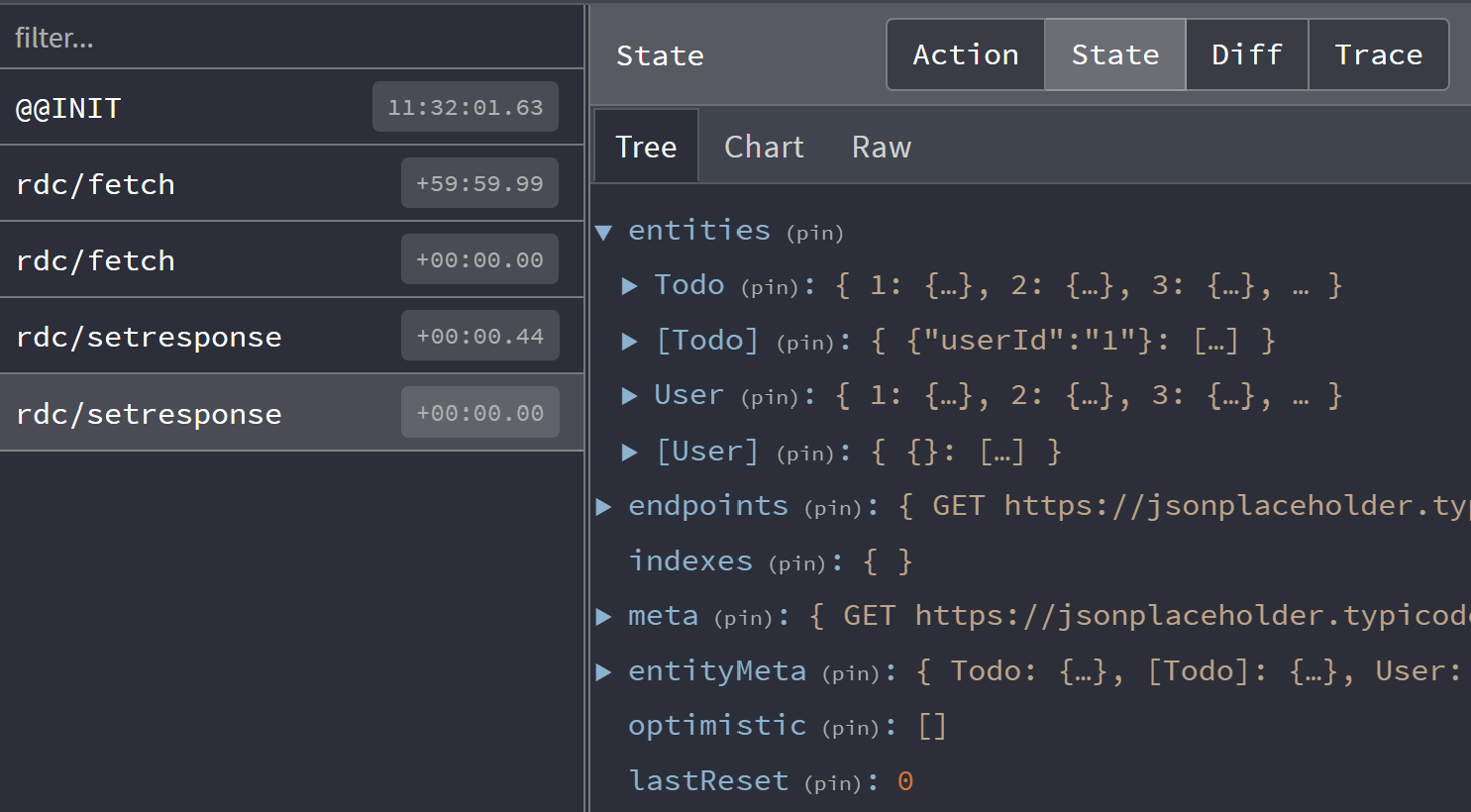
Click on the 'state' tab in devtools to see the store's entire state. This can be useful to determine exactly where data is. There is also a 'meta' section of the cache for information like when the request took place (useful for TTL).
State Diff
For monitoring a particular fetch response, it might be more useful to see how the store updates. Click on the 'Diff' tab to see what changed.
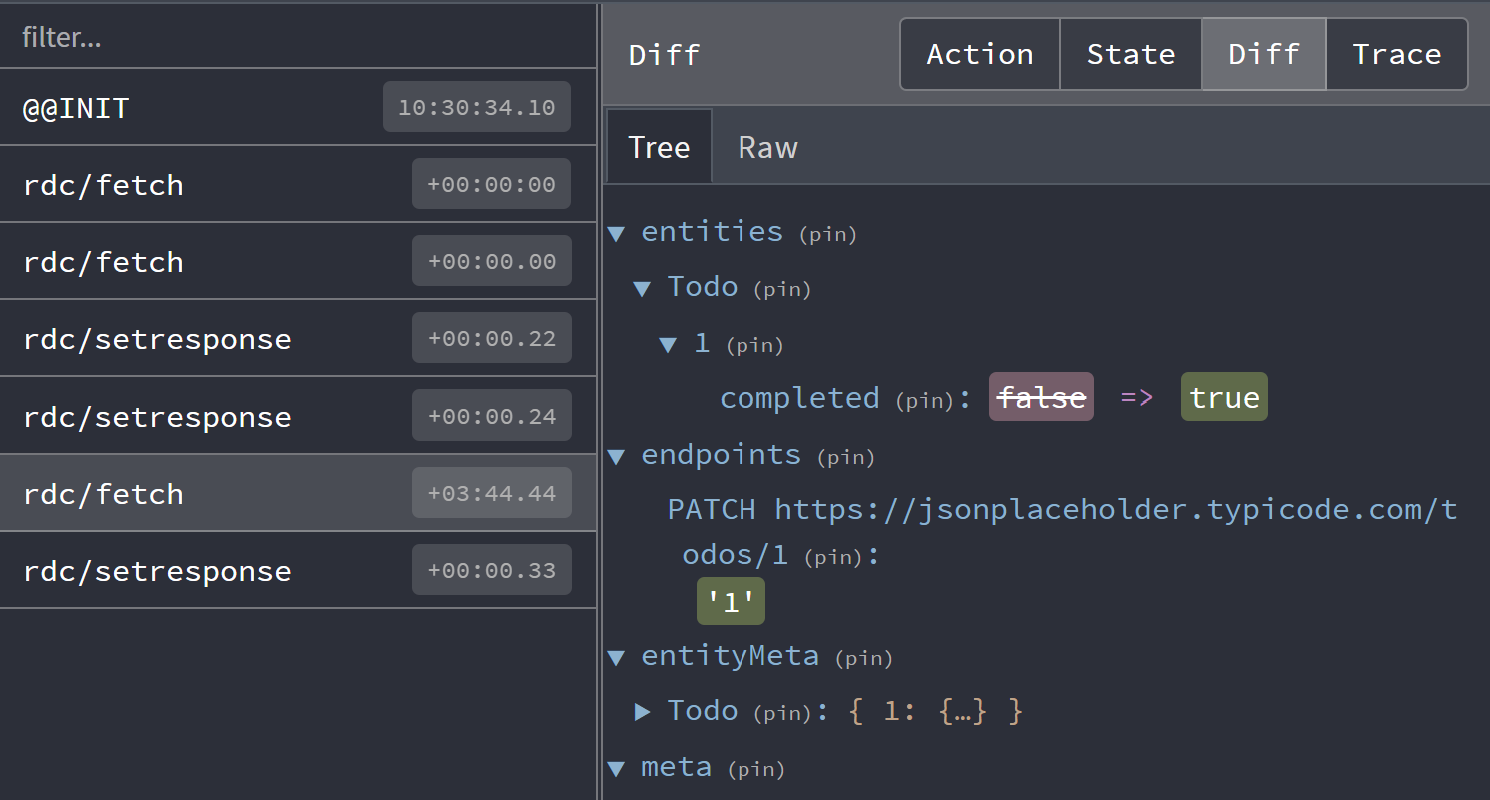
Here we toggled the 'completed' status of a todo using an optimistic update.
Action Tracing
Tracing is not enabled by default as it is very computationally expensive. However, it can be very useful
in tracking down where actions are dispatched from. Customize DevToolsManager
by setting the trace option to true with getDefaultManagers:
import {
DevToolsManager,
DataProvider,
getDefaultManagers,
} from '@data-client/react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
const managers = getDefaultManagers({
devToolsManager: { trace: true },
});
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.body).render(
<DataProvider managers={managers}>
<App />
</DataProvider>,
);